Building an OCI-native Container Image CI/CD Pipeline¶
An OCI-native secure container image build/delivery pipeline using the following tools:
The Open Container Initiative (OCI) is an open governance structure for the express purpose of creating open industry standards around container formats and runtimes.
This document describes a step-by-step procedure towards achieving an OCI-native secure software supply chain using zot in collaboration with other opensource tools. The following diagram shows a portion of the CI/CD pipeline.
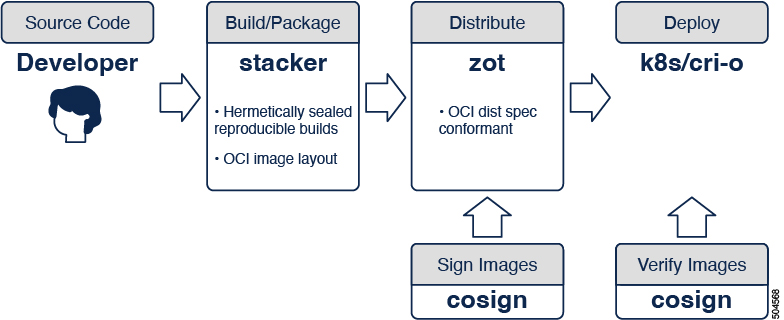
Build images¶
stacker is a standalone tool for building OCI images via a declarative yaml format. The output of the build process is a container image in an OCI layout.
example: stacker build command
stacker build -f <stackerfile.yaml>
Image registry¶
zot is a production-ready vendor-neutral OCI image registry server purely based on the OCI Distribution Specification. If stacker is used to build the OCI image, it can also be used to publish the built image to an OCI registry.
example: stacker publish command
stacker publish --url <url> --username <user> --password <password>
Alternatively, you can use skopeo, a command line utility that performs various operations on container images and image repositories.
example: skopeo copies an image to a registry
skopeo copy --format=oci oci:<oci-dir>/image:tag \
docker://<zot-server>/image:tag
Click here to view an example of pushing and pulling an image using skopeo.
Signing images¶
cosign is a tool that performs container signing, verification, and storage in an OCI registry.
example: cosign generates keys and signs an image in the registry
cosign generate-key-pair
cosign sign --key cosign.key <zot-server>/image:tag
Click here to view an example of cosign operations.
Deploying container images¶
cri-o is an implementation of the Kubernetes Container Runtime Interface (CRI) to enable using OCI compatible runtimes. It is a lightweight alternative to using Docker as the runtime for Kubernetes.
zot is compatible with kubernetes/cri-o using
docker://transport, which is the default.
example: kubelet configuration file
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: example-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: example-container
image: <zot-server>/image:tag
Container image verification¶
cosigned is an image admission controller that validates container images before deploying them.
example: install cosigned using Helm
kubectl create namespace cosign-system
kubectl create secret generic mysecret -n \
cosign-system --from-file=cosign.pub=./cosign.pub
helm repo add sigstore https://sigstore.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
helm install cosigned -n cosign-system sigstore/cosigned \
--devel --set cosign.secretKeyRef.name=mysecret